We examined Hotchkiss Drive in detail in the last lesson, and we will discuss Torque Tube Drive in today's lecture.
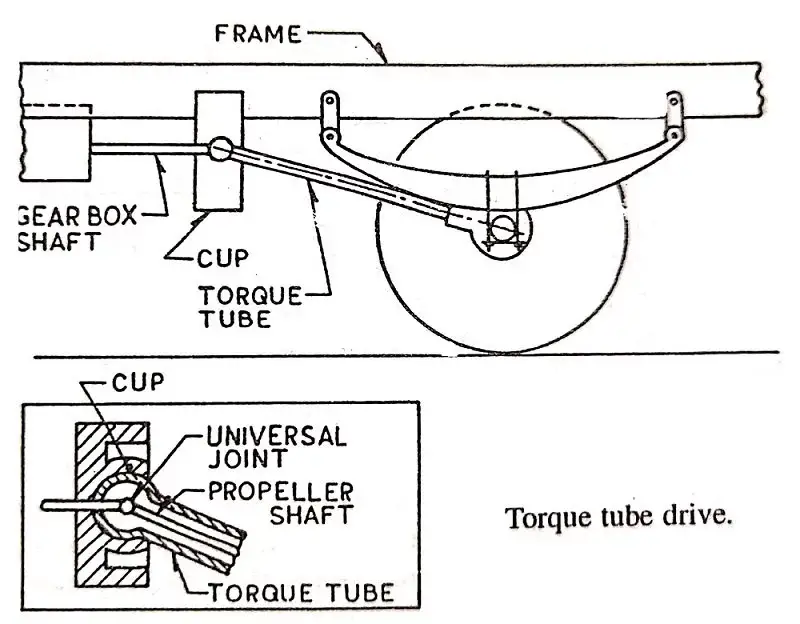
Line Diagram of Torque Tube Drive:
The following is a line diagram of Torque Tube Drive.
Parts of Torque Tube Drive:
The parts of Torque Tube Drive are as follows.
- Torque Tube
- Shackle -2 No's
- Universal Joints – 1 No’s
- Sliding Joint
- Propeller Shaft
- Bevel Pinion Shaft
- Rear Axle Casing
- Wheel of the Vehicle
- Leaf Spring
- Frame
An Explanation for the parts of Torque Tube Drive:
Everything was explained in the Hotchkiss Drive, with the exception of a few bits listed here. So just think about it.
Torque Tube:
There was no need for a Sliding joint on the Propeller shaft because it was only present inside the Torque Tube.
Shackle:
In comparison to Hotchkiss Drive, the spring is held in place by two shackles that are attached to the vehicle's frame.
Universal Joint:
At first, just one Universal Joint is employed, and it is located inside the torque tube. The universal joint connects two shafts whose axes are at an angle to one another.
Sliding Joint:
Because both the propeller shaft and the pinion shaft will travel around the same centre, there is no need for a sliding joint, as mentioned in the Torque Tube drive's operation.
Working Principle of Torque Tube Drive:
The Torque Tube Drive works on the following premise.
One end of the torque tube, which has a spherical shape, is placed in the cup, while the other end is attached to the axle casing.
The Torque tube is encased in the propeller shaft and receives the torque reaction.
As a result, the bevel pinion shaft's centerline will not vary, and it will always pass through the centre of the spherical cup.
There is no need for the universal joint at the rear end of the propeller shaft if the propeller shaft is connected to the shaft of the gearbox using a universal joint located in the centre of the spherical cup.
There is also no need for a sliding joint because both the propeller shaft and the pinion shaft will rotate around the same axis, namely the spherical cup's centre.
The Torque reaction and driving thrust are exclusively taken by the Torque tube, as can be seen from the above.
Advantages of Torque Tube Drive:
The advantages of Torque Tube drive are as follows.
- The Propeller shaft was present inside the Torque Tube only and there is no need for a Sliding joint on the Propeller shaft.
- In these drives, the side thrust and the weight of the body are taken up by the springs.
Disadvantages of Torque Tube Drive:
The disadvantages of Torque Tube drive are as follows.
- If Coil springs are used instead of Leaf springs then they are not able to take side loads and therefore there is a need to employ a new member which is usually in the form of a transverse radius rod called Panhard rods.
- These rods are fixed parallel to the wheel axis whose one end is pivoted to the axle casing and the other end is connected to the chassis frame.
Applications of Torque Tube Drive:
The applications of Torque Tube Drive are as follows.
- The Chevrolet Chevette used a torque tube from 1976-1988.
- The Chevrolet Corvette has used a torque tube Since 1996 and has introduced in the 1997 model for the C5 version.