Introduction
In today's digital age, the computer stands as one of the most remarkable and transformative inventions in human history. From powering space exploration to simplifying everyday tasks, computers have become an indispensable part of modern life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essence of a computer, its fundamental components, historical evolution, and its profound impact on society.
I. Understanding the Concept of a Computer
At its core, a computer is a sophisticated electronic device capable of receiving, processing, storing, and outputting data. Unlike traditional tools, computers possess the unique ability to execute complex operations by following sets of instructions called programs. These programs allow users to harness the immense processing power and versatility of computers to perform tasks that range from basic calculations to intricate simulations and artificial intelligence.
II. The Key Components of a Computer
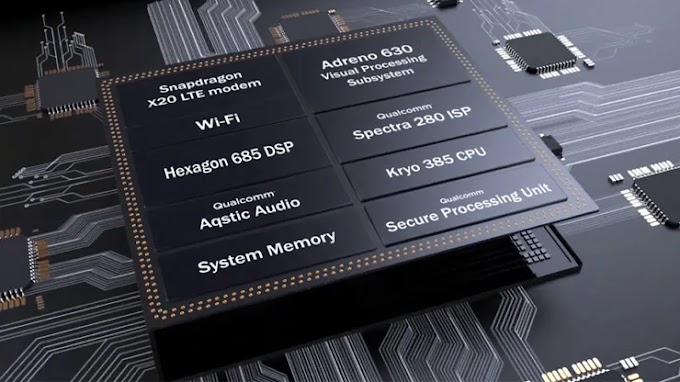
A. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU serves as the "brain" of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and controlling the overall operation of the system. It performs arithmetic, logical operations, and manages data movement within the computer's internal memory.
B. Memory (RAM and Storage)
Random Access Memory (RAM) provides temporary storage for data and programs that are actively being used by the CPU. On the other hand, storage devices like hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs) offer long-term data retention.
C. Input and Output Devices
Input devices, such as keyboards, mice, and touchscreens, enable users to interact with the computer by providing data and commands. Output devices, including monitors, printers, and speakers, display or produce results from the computer's processing.
III. The Historical Evolution of Computers
The roots of computing can be traced back to ancient devices like the abacus, but the development of modern computers began in the 19th and 20th centuries. Pioneering efforts, such as Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Ada Lovelace's visionary concepts, laid the groundwork for computational theory.
The first electronic computers emerged during the mid-20th century. The famous ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) marked a significant breakthrough in electronic computing, paving the way for rapid advancements in the decades to come.
The subsequent generations of computers saw exponential improvements in processing power, miniaturization, and portability. From mainframes and minicomputers to personal computers, laptops, and smartphones, each iteration of computers has brought unprecedented accessibility and convenience to users worldwide.
IV. Impact on Society
The proliferation of computers has revolutionized virtually every aspect of human life. The rise of the internet and global connectivity has transformed how we communicate, share information, and conduct business. E-commerce, social media, and online education are just a few examples of how computers have reshaped industries and society as a whole.
Moreover, computers have revolutionized scientific research, engineering, medicine, and entertainment. They have enabled sophisticated simulations, data analysis, medical imaging, and immersive gaming experiences that were once unimaginable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a computer is a remarkable invention that has redefined the way we live, work, and interact with the world. Its ability to process vast amounts of information, coupled with its versatility, has opened doors to endless possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, the computer's impact will only grow, driving innovation and shaping the future of humanity. Embracing the potential of this powerful tool is essential to staying relevant in an increasingly digital world.