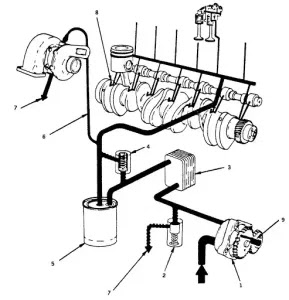
An engine uses gasoline to generate energy that allows a car to run. In India, modern vehicle engines usually use fuels such as petrol, diesel, compressed natural gas (CNG), and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
Petrol or petrol is ignited in the internal combustion engine, where it combines with air to produce energy that turns the wheels in petrol engines. The purpose of this blog is to discuss the fuel supply systems in petrol engines.
What Are Fuel Systems in Car Engines?
A petrol engine's fuel delivery system is made up of many components that work together to send a predetermined amount of fuel from the car's fuel tank to the engine for combustion. A fuel tank, fuel pump, carburettor, fuel injectors, fuel filters, and fuel lines are among the components.
This system's principal job is to store and supply fuel to the engines. Fuel pumps extract petrol from the tank and deliver it to the injector via fuel lines. The fuel injection system delivers the necessary fuel to the engine for combustion.
What Are the Types of Fuel Supply Systems in Petrol Engines?
The following are the numerous types of gasoline supply systems found in modern cars with petrol engines:
1. Gravity system
In this fuel system, the manufacturers put the gasoline tank at the highest position of the spark-ignition engine. Gravity causes petrol to fall into the carburetor from its highest location. The mechanisms of this fuel system are exceedingly basic and affordable. As a result, gravity systems can be found in compact engines that consume less fuel. Furthermore, manufacturers do not produce good heads for huge engines.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
2. Pressure system
Car manufacturers install a pressure seal tank or an airtight tank next to a car's engine or under the seat in this gasoline system. A pump uses air to build pressure and then pushes petrol into the combustion chamber.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
3. Pump system

This gasoline delivery system includes a steel pipe that transports petrol to the fuel pump. This fuel pump then injects petrol into the float chamber within the carburettor through another steel pipe. Mechanical, electrical and diaphragm pumps now supply petrol from the fuel tank.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
4. Fuel Injection System

This fuel supply system is most common in current automobiles. The air injector nozzle in this arrangement atomises gasoline from the fuel tank and sends these particles into the air stream. Manufacturers may utilise separate injectors for each cylinder or a single injector for all cylinders.
Advantages:
- Fuel injection systems are advanced, and, as a result, they are the most accurate among all other systems.
- Such systems can quickly warm up and start a car’s engine.
- Fuel injection system enables engines to develop high power.
- These consume less petrol in certain instances.
Disadvantages:
- Setting up this fuel supply system can be quite expensive initially.
- In some cases, petrol backflows can occur.
What Are the Various Components of a Fuel Supply System?
1. Fuel Tank
The fuel tank of a car holds and stores fuel in order for the automobile to run. Petrol will not be able to pass freely to the combustion chamber if a petrol tank is leaking or clogged. As a result, the appropriate operation of this component of a vehicle is critical since it aids in the smooth operation of the vehicle.
2. Fuel Pump
The fuel pump's job is to deliver petrol from the fuel tank to the fuel injectors. It transports this fuel via fuel lines. In petrol engines, a fuel pump is present, however in diesel engines, the injector sends petrol directly to the carburetor. Furthermore, there are two types of fuel pumps: mechanical pumps and electrical pumps.
3. Fuel Injector
The function of a fuel injector is to inject fuel into a carburetor or a car's combustion chamber. This part consists of a valve with a long nozzle that produces fuel sprays and air droplets.
4. Carburetor

Carburetors are usually seen in older petrol engines. After the fuel injector transfers petrol, a carburetor forms an air and fuel mixture. The mixture is then sent to a car's combustion chamber after it has thoroughly combined fuel and air from the surroundings.
5. Fuel Filter

A gasoline filter is essential within a petrol engine. gasoline injectors are not very sturdy, therefore they are easily destroyed by debris and gasoline particles. The duty of the fuel filter is to remove trash and fuel particles from the tank and pump. To catch these particles, it is put between the pump and the tank.
6. Fuel Lines

In petrol engines, fuel lines serve as a link between all of the other components of the fuel supply system. It connects the petrol tank to the fuel injector, as well as the engine tank to the engine.
7. Fuel Gauge

The fuel gauge is a dial that displays the quantity of petrol remaining in a vehicle's fuel tank. It's simply accessible on your car's dashboard. The fuel gauge in older cars did not always indicate the real quantity of petrol in the tank, but in newer cars, the portrayal is very accurate.
8. Emission Vapour Control System

The job of the emission vapour controls is to prevent fuel vapours from being emitted into the vehicle's ambient air. If this component fails, it might cause an unpleasant odour to develop inside the car. Furthermore, it is detrimental to the environment and can cause problems with the engines' general performance.
9. Fuel Pressure Regulator

The fuel pressure regulator keeps the engine's pressure stable. Because it is present in petrol engines, fuel injectors have higher pressure than combustion chambers.
Now that you've learned about all of the components of a fuel supply system for petrol engines, let's look at the various supply systems.
What Are the Factors Which Determine the Quality of Fuel?
Before learning about the numerous types of gasoline delivery systems that transfer petrol or any other sort of fuel to a car's engine, it's important to understand the various components that define the fuel's quality. These are the determining factors:
Volatility- The volatility of petrol is a key determining element because it affects the performance of your vehicle's engine. Furthermore, fuel volatility influences various other factors:- The ease at which drivers can start their vehicle
- Vapour lock forming in a fuel supply system
- Acceleration of a car’s engine
- Percentage of crankcase oil dilution
- Circulation of petrol in a multi-cylinder engine
Ignition Quality- The ease with which oil can burn in a vehicle's combustion chamber is referred to by this phrase. Furthermore, specialists employ octane and cetane numbers to determine the ignition quality of petrol. Both octane and cetane are used to assess the knock characteristics of automobile fuel.
Calorific Value- When petrol causes combustion, it generates heat in a car engine, which is referred to as the heat or calorific value of the fuel. Calorific value is important since it helps measure petrol quality because heat is what drives an engine.