Automobile developers have been creating and marketing hybrid vehicles since the late 1800s; yet, due to the increased cost needed in mass production, its market acceptance remains low. However, automakers are continuing to research and develop improved hybrid technologies in order to meet rigorous emissions standards. But what exactly is a hybrid car? Continue reading to learn more about the different types and benefits of hybrid vehicles, as well as the distinction between hybrid and electric vehicles.
What is a Hybrid Car?
Hybrid vehicles are propelled by two engines: one petrol and one electric. Both operate together to turn the wheels. As a result, less petrol is burned, resulting in improved fuel efficiency. Hybrids outperform traditional vehicles in terms of power and fuel efficiency because they combine the benefits of high fuel efficiency and low emissions. Excess power generated by hybrid vehicles when traveling or braking is used to charge the batteries. This, in turn, contributes to increased fuel efficiency or range.
How Do Hybrid Electric Cars Work?
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), sometimes known as hybrid automobiles, are powered by an internal combustion engine (petrol engine) and at least one electric motor. Continue reading to learn more about hybrid electric vehicles.
Hybrid Vs. Electric Cars:
The fundamental distinction between a hybrid and an electric vehicle is that the hybrid uses both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor(s) to power its wheels. The electric car, on the other hand, gets its power from a single source: the electric motor(s).
While hybrid vehicles provide higher fuel efficiency or longer distances/ranges, electric vehicles have yet to reach their full potential. Nonetheless, electric vehicles emit fewer pollutants than hybrid vehicles that rely on an internal combustion engine.
Difference Between Hybrid and Electric Cars:
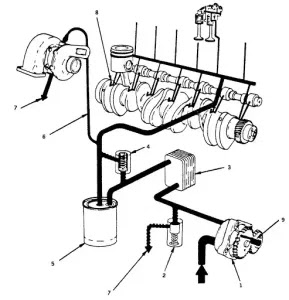
Key Components of Hybrid Electric Cars:
Below are the main components that help generate power to propel the hybrid car:
Internal Combustion Engine:
In a regular petrol engine, fuel is injected into the internal combustion chamber. Here, fuel mixes with air and is ignited by a spark plug.
Electric Traction Motor:
This motor draws power from the battery pack and sends power to the wheels.
Electric Generator:
This sort of motor creates electricity from braking energy, which recharges the battery pack. Some generators perform both driving and regenerative functions.
Traction Battery Pack:
The pack stores electricity to run the electric motors and recharges via the generator.
The internal combustion of the petrol engine continues to be the hybrid car's principal source of power. The electric motor is powered by regenerative braking, but the hybrid's battery pack cannot be recharged without the primary gasoline engine.
Types of Hybrid Cars:
Automobile manufacturers utilize various hybrid designs to attain optimal fuel efficiency or to keep hybrid car pricing as low as feasible. The following are the various types of hybrid vehicles:
1) Parallel Hybrid:
The parallel hybrid is the most common hybrid design, using both electric and internal combustion engines to power the vehicle. They can run in tandem or one can be utilised as the primary power source while the other kicks in when more power is necessary, such as while climbing a slope or passing another vehicle. Because both power sources are connected to the gearbox or gearbox in tandem, they are referred to as "parallel." Toyota Camry, Honda Accord, Toyota Prius, Hyundai Sonata, and other parallel hybrid vehicles are examples.
2) Series Hybrid:
The Series Hybrid is a hybrid car that uses both a gasoline internal combustion engine and an electric motor. The internal combustion engine, on the other hand, does not propel the vehicle; instead, it creates electricity to recharge the battery pack. The battery pack then powers the electric motor(s), which then powers the wheels. The BMW i3, Kia Optima, Ford Fusion, Chevrolet Volt, and other Series Hybrid vehicles are examples.
3) Plug-in Hybrid:
The Plug-in Hybrid elevates the ordinary hybrid vehicle by incorporating a considerably larger battery pack that must be charged. In general, it charges the battery pack using a 110-volt electrical connector, comparable to an electric automobile. Because the Plug-in Hybrid automobile has an internal combustion engine and may be driven once it has been fully charged, the vehicle's fuel efficiency improves significantly. The BMW 330e, Hyundai Ioniq Plug-in Hybrid, Volvo XC40 Recharge Plug-in Hybrid, and other plug-in hybrid vehicles are examples.
4) Two-Mode Hybrid:
This form of hybrid design functions in two ways. In the first mode, it functions exactly like a standard hybrid card. In the second mode, the design can be adjusted by the engine to fit various vehicle tasks.
5) Mild-Hybrid:
In recent years, the cost of building an efficient hybrid car has remained high. Car manufacturers are developing new tactics to bring hybrid technology to the general public. Car manufacturers have used mild-hybrid designs in order to meet emission standards while also marginally improving fuel efficiency without significantly increasing the cost. In this sort of hybrid, the electric motor works alongside the gasoline engine to improve fuel efficiency, performance, or both. It also serves as a starter for the automatic start/stop function, which turns off the engine when the vehicle comes to a halt, reducing fuel consumption. Maruti Suzuki Ertiga, Ciaz, and Baleno are examples of mild-hybrid vehicles.
List of Hybrid Cars:
Below is the list of hybrid cars that are popular in the world:
Toyota Prius
Ford Fusion Hybrid
Toyota Camry
Honda Accord
Hyundai Ioniq
Toyota Corolla
BMW i8
Honda CR-Z
Kia Optima
Hyundai Sonata
List of Upcoming Hybrid Cars in India 2020:
Below is the list of upcoming hybrid cars in India in 2020:
Hyundai Ioniq
Expected Price: Rs.20 lakh
Expected Launch: End of 2020
Nissan Leaf
Expected Price: Rs.30 lakh
Expected Launch: Early 2021
BMW i8
Expected Price: Rs.3 crore
Expected Launch: Late 2020
Volvo XC60 Plug-in Hybrid
Expected Price: Rs.90 crore
Expected Launch: Early 2021
BMW i3
Expected Price: Rs.1 crore
Expected Launch: Mid-2021
List of Cheapest Hybrid Cars:
Below is the list of cheapest hybrid cars available in the global market:
Toyota Corolla
Hyundai Ioniq
Toyota Prius
Kia Niro
Hyundai Ioniq Plug-in Hybrid
Toyota C-HR
List of Hybrid Cars in India 2020:
Toyota Camry
MG Hector
Honda Accord
Toyota Vellfire
BMW 7 Series
Toyota Prius
Volvo XC90
Lexus LC
Lexus RS
Lexus NX
List of Mild-Hybrid Cars in India:
Below is the list of mild or smart hybrid cars in India which do not use an electric motor to propel the car but aid in saving fuel:
Maruti Suzuki Ertiga
Maruti Suzuki Ciaz
Maruti Suzuki Baleno
Toyota Glanza
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Cars:
Hybrid automobiles may serve as a stepping stone before the automobile industry transitions to all-electric vehicles. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of hybrid vehicles can help you grasp the technology.
Pros of Hybrid Cars:
Cleaner Emission: In contrast to internal combustion engines, hybrid vehicles use both electric and internal combustion engines. As a result, emissions are reduced and the environment is protected.
Less Fuel Dependency: There is more power available with an electric motor to supplement the basic petrol engine. As a result, there is reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Smaller and Efficient Engine: Because there is an electric motor, smaller engines do not have to power the hybrid automobile alone. In addition, the petrol engines utilised in hybrid vehicles are smaller and more fuel efficient.
Regenerative Braking: When a hybrid vehicle's brake is applied, the electric generator generates electricity and recharges the battery. This avoids the need to come to a complete stop in order to charge the battery pack.
Cons of Hybrid Cars:
Lower Performance: Because the major goal is to improve the hybrid car's fuel efficiency or range, the power or acceleration may lag behind a normal internal combustion engine automobile.
Expensive to Buy: Despite efforts by automakers to close the price gap between conventional and hybrid vehicles, hybrids continue to command higher prices.
High Maintenance Cost: With multiple mechanical elements in automobiles and two sets of engines powering the hybrids, maintenance costs remain considerable. Furthermore, not all mechanics are trained to work on hybrid vehicles.